Necessity & Importance of Nepali Locale and Unicode Standard for Nepalese Government Employees
Background
Nepal, with its diverse cultural and linguistic landscape, designates Nepali as the official language for government operations and public administration. As Nepal progresses towards a more digitized infrastructure, the integration of technological solutions that support the Nepali language and regional settings becomes increasingly essential. Government employees are pivotal in implementing and managing these digital systems, making it crucial that the tools they use accommodate Nepal's linguistic and cultural specifics.
Despite significant advancements, many existing systems within government agencies are not fully adapted to handle Nepali text and locale-specific settings effectively. This inadequacy can lead to issues such as incorrect data representation, miscommunication, and inefficiencies in managing official documents and public interactions. To address these challenges, it is essential to integrate Nepali Locale and Unicode into government systems. This integration ensures that digital tools align with the country's linguistic requirements and enhance the efficiency of government operations in Nepali local language.
Introduction
The integration of Nepali Locale and Unicode into government operations is a fundamental step in ensuring that digital tools meet Nepal's linguistic and cultural needs. Nepali Locale settings are designed to customize digital systems according to regional conventions such as date formats, number formatting, and currency symbols. This customization is crucial for generating and managing documents that are both accurate and culturally relevant.
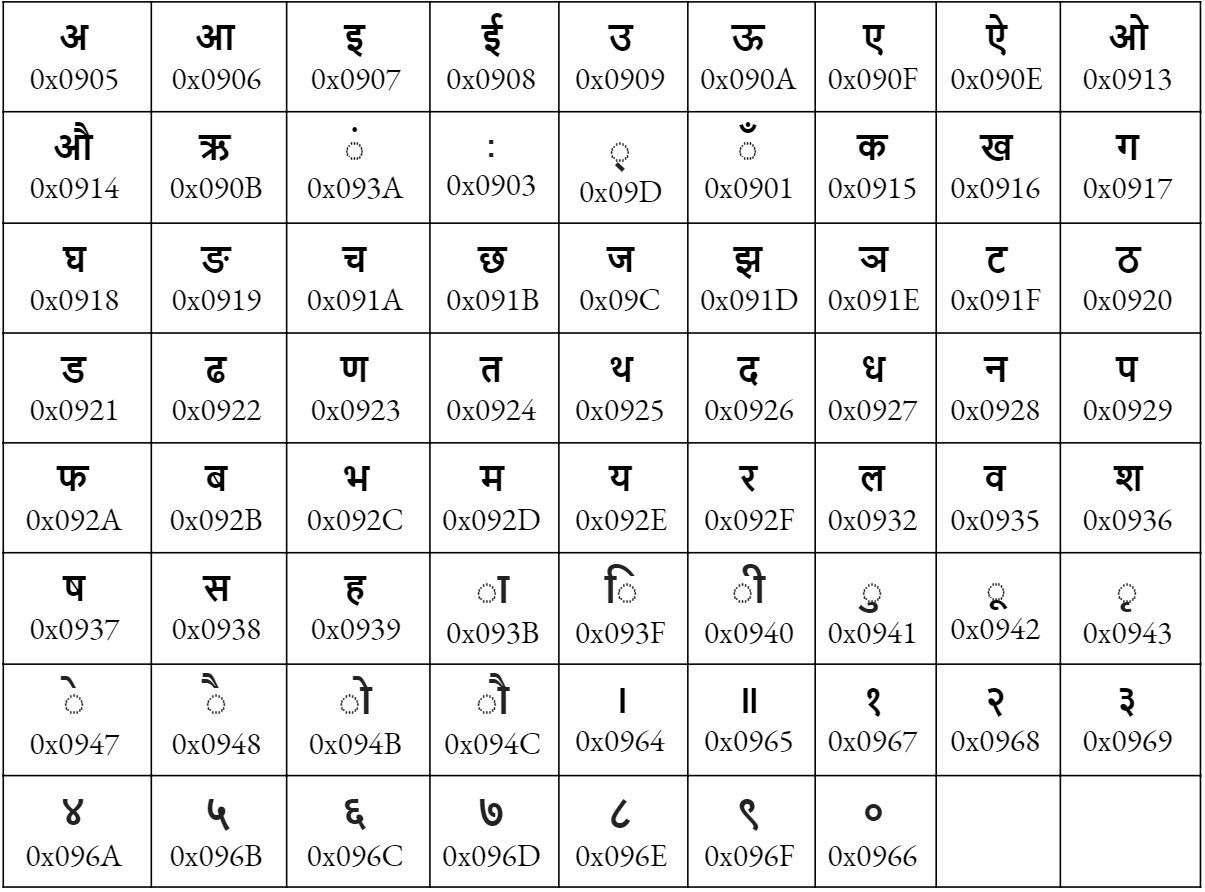
Unicode, on the other hand, is a universal character encoding standard that provides a consistent way of representing text across different digital platforms. By adopting Unicode, government systems can avoid errors related to text encoding, ensuring that Nepali characters are displayed correctly across various devices and applications. This is vital for maintaining the integrity of official communications and public records, ensuring that all textual information is accurately represented and accessible. This duly ensures that the Nepali text is stored in Nepali characters to represent as data and can be search index and manage in computational formats.
1. Enhancing Accurate Communication
Official Documentation: Government employees frequently handle a variety of official documents, reports, and communications in Nepali. The use of Unicode in these documents ensures that all characters are displayed correctly, which is crucial for preventing errors and misunderstandings. Standardizing text representation with Unicode helps maintain the integrity of official records by ensuring that documents are consistently rendered across different systems and devices. And the storing of data for further processing will be same across all platforms and devices. Thus, uniformity of the Nepali text ensures correct and properly transferred text worldwide.
Public Interaction: Government employees who interact with the public—through notifications, announcements, and service portals—need to ensure that their communication is clear and accurate. Unicode plays a significant role here by making Nepali text readable and understandable. This clarity fosters better engagement with the public and improves the overall effectiveness of service delivery. Accurate and accessible communication is essential for building trust and ensuring that citizens can easily access and understand government services without any errors or misrepresentations.
2. Improving Data Management and Processing
Data Entry and Retrieval: Government databases often contain vast amounts of data in Nepali. Nepali Locale settings are crucial for ensuring that data such as date formats, numerical information, and other locale-specific details are consistent and accurately interpreted. Implementing standards will ensure all the data from various systems are all represent the same encoded format to save, retrieve and use. This reduces errors in data entry and retrieval, which is critical for accurate reporting and informed decision-making. Proper data management supported by Nepali Locale settings enhances the reliability of government records and databases.
Standardization Across Systems: The use of Unicode and Nepali Locale settings helps standardize data across various systems and platforms used by government agencies. This standardization is essential for integrating data from different sources and ensuring its reliability and accuracy. By maintaining consistency in data representation, government agencies can more effectively consolidate and analyze information, leading to better-informed decisions and more efficient operations. This will help to centralized the data with interoperability between any IT system and devices that e-governance services can be deployed with complete and comprehensive data of all the citizens for any services provided to public.
3. Facilitating Inclusivity and Accessibility
Language Representation: The adoption of Nepali Locale and Unicode ensures that digital platforms are accessible to Nepali-speaking citizens. This inclusivity is crucial for ensuring that all members of the public can interact with government services in their native language. Enhanced accessibility fosters greater equity in public services and ensures that language barriers do not impede the ability of citizens to engage with government processes.
User Experience: For government employees, using systems with familiar locale settings can greatly improve their daily work experience. Nepali Locale settings make digital interfaces more user-friendly, reducing confusion and increasing efficiency. This will even help employees to understand and deliver service using local and native language. When employees are comfortable with the digital tools they use, they are more likely to perform their tasks effectively and contribute to a smoother functioning of government operations and services provided.
4. Addressing Current Challenges
Awareness and Training: One of the primary challenges is that many government employees may not fully understand the importance of Nepali Locale and Unicode. Providing targeted training and resources is essential to help them grasp how these tools enhance their work and improve public service delivery. Awareness programs should emphasize the benefits of these technologies and how they can streamline operations and enhance communication. This will benefit for providing errorless services.
System Integration: Legacy systems that do not support Unicode and Nepali Locale can pose significant challenges. Transitioning to updated systems that are compatible with these standards is necessary for resolving compatibility issues and facilitating smoother digital interactions. Ensuring that all systems are up-to-date and capable of handling Nepali text and locale settings will enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of government operations.
Security and Compliance: Ensuring the security and compliance of digital content is also crucial. Unicode and Nepali Locale settings contribute to data security and proper encoding, reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring adherence to legal and regulatory requirements. Implementing these standards helps protect sensitive information and ensures that government systems comply with established data protection norms.
5. Hypothesis that Employees Do Not Learn
A common hypothesis is that government employees may be reluctant to adopt Nepali Locale and Unicode due to inadequate training or a lack of awareness about the benefits. If employees are not provided with comprehensive training or if the advantages of these tools are not effectively communicated, they may view them as unnecessary or overly complex. To address this issue, it is essential to develop targeted educational programs and awareness campaigns that highlight the practical benefits and ease of using these technologies. Ensuring that employees understand the value of Nepali Locale and Unicode will increase their willingness to embrace and utilize these tools. Apart from training all the system must comply to use the Nepali Locale and Unicode standards efficiently and measures should be taken to use and promote the standards by all government employees.
6. How Long Nepali Government Employees Should Be Taught Locale and Nepali Unicode
The fundamentals of the standards should be given to all employee and continuous learning and adaptation are crucial for government employees to maintain effective skills in digital operations. Rather than a one-time training session, employees should engage in ongoing education to stay current with technological advancements and evolving requirements with involvement in their day-to-day operations to provide better and efficient services.
Continuous Training: Government employees should participate in periodic training sessions to refresh their knowledge and adapt to updates in locale settings and Unicode standards. This ongoing education helps ensure that they remain proficient and up-to-date with best practices, which is essential for maintaining high standards in digital operations.
Regular Updates: As digital tools and technologies evolve, it is important for employees to receive timely updates and training on new features and improvements related to Nepali Locale and Unicode. Regular updates will help employees stay informed about the latest developments and ensure that they can effectively utilize new functionalities and involvement with the technology trend will enhance their skill set and would provide better feedback to improve further in the systems and their own knowledge.
Long-Term Engagement: Establishing a culture of continuous learning within government institutions promotes long-term engagement with technological advancements. This approach reduces resistance to change and encourages the efficient use of digital systems. A well-structured training program, possibly spanning several weeks, can ensure that employees become proficient with Nepali Locale and Unicode. Regular refresher courses and updates on new developments can help maintain their skills and awareness over time. The support helpdesk should be readily available to all employees delivering services to resolve any issues or problems arise which will encourage to use the standardized system with confidence to deliver quality service to public.
Conclusion
Integrating properly enhanced standard settings of Nepali Locale and Unicode into government operations represents more than just a technical upgrade; it is a strategic move towards improving the effectiveness and exclusivity of government services. While there are challenges in achieving employee buy-in, a focused approach to training and awareness can overcome these barriers. By embracing Nepali Locale and Unicode, Nepalese government employees can enhance communication, data management, and public service delivery, leading to a more efficient and accessible government services. This integration will ultimately contribute to a more streamlined and effective operation of government services, benefiting both employees and the public.



